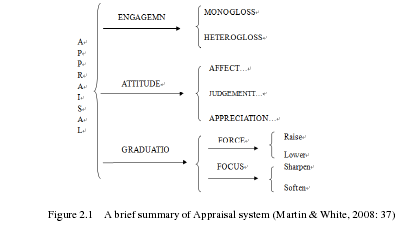
According to Halliday, language serves threemetafunctions, namely, ideational, interpersonal and textual metafunctions. Among them,interpersonal function enables one to use language to interact with others, maintainrelationships, convey attitude toward worldly things, and then influence others viewpoints(Halliday, 1978:112). According to Halliday, interpersonal meaning is mainly realized bygrammatical means as mood and modality at syntax level. However, with the increasedstudies on interpersonal meaning, some scholars found that SFL put too much emphasis onexchange of meanings, i.e. information, goods and services, while little attention has beenpaid to evaluative function of language which is generally expressed by lexical choices andfew grammatical structures (Thompson 2000:65).J.R. Martin, an Australian linguist, found the missing link along with Peter White andproposed a new lexicon—grammatical framework called Appraisal Theory in 1990s. It isconcerned with “the kinds of attitude that are negotiated in the text, the strength of thefeelings involved and the ways in which values are sourced and readers aligned ” (Martin,2003:22). Appraisal Theory aims to examine the semantic evaluation in discourse, which isconsidered as more systematic as well as comprehensive than former related studies onattitudinal meaning as it contributes a lot to the categorization of appraisal lexicon (ZhangDelu & Liu Shizhu, 2006). It deals with the vocabulary choices selected to negotiate andexpress attitudes, stance and viewpoints, extending the scope of interpersonal meaning atlexical level. In other words, Appraisal Theory concentrates on how speakers/writers tactfullyuse language resources to pass JUDGMENTs on human behavior, objects and events, alignwith those who share similar ideas, influence attitudes of neutral hearers/readers, and keepdistance with those who see things differently. Martin & White (2008) classified AppraisalTheory into three subsystems, that is, Attitude, Engagement and Graduation. To be specific,Attitude is the core of evaluation while Engagement assists the whole system in dealing withthe source of attitudes, and Graduation stretches across the whole appraisal system modifyingAttitude and Engagement in different degrees. Specifically, the three subsystems can still befurther divided as the following figure shows.
.........
2.2 Studies of Sports News
In this part, the author first gives an account of the definition of news and sports news,and then offers the features as well as classification of sports news. Afterwards, a reviewingpart about previous studies on sports news both at home and abroad will be followed.In past few decades, many experts and scholars had tried to define news from the pointof form and content of news. Some emphasize the form of news. For instance, news is brieflydefined as information or reports about recent events in Cambridge Dictionaries. Meanwhile,a great number of scholars tend to stress the attractiveness of content in news. For example,Burton Rascoe, the American editor and literary critic of the New York Herald Tribune holdsthat “a news sense is really a sense of what is important, what is vital, what is color of life—what people are interested in” (Burton Rascoe, 1922). And according to Laurence & Roland,News refers to “an account of current ideas, events or problems that interests people”(Laurence R Campbell & Roland E Wolseley, 1993), which emphasizes the timeliness as wellas interest of news. Moreover, a witty but incisive definition was once given by John Bogartin The New York Sun, “when a dog bites a man that is not news, but when a man bites a dogthat is news” (Mencher, 19



